12 cases of fraudulent invoices were sentenced to probation and detention for illegal purchase of VAT invoices
In practice, due to the difficulty in obtaining input invoices for bulk commodities, some enterprises chose to obtain VAT invoices by opening or purchasing on behalf of others in order to make up for the shortfall of inputs, and a large number of criminal cases broke out as a result. The author searched such tax-related cases and found that there were similarities in the business mode and behavior involved in such cases, but the final court judgment was "different judgments for the same case", in which most of the judgments were that it constituted the crime of falsely issuing VAT invoices, and some of the judgments were that it constituted the crime of illegally purchasing VAT invoices, while the crime of falsely issuing VAT invoices was that it constituted the crime of illegally purchasing VAT invoices. Most of the judgments are considered to constitute the crime of false invoicing of VAT, and some of them are considered to constitute the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices, while the maximum penalty for the crime of false invoicing of VAT is life imprisonment and the maximum penalty for the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices is five years' imprisonment, which is a big difference between the two. The author searches for the public cases, sorts out the views of the courts and combines them with the objective problems in practice, in order to give the enterprises certain reference suggestions for the benefit of the readers.
I. Summary: Obtaining false invoices to be convicted and sentenced for the crime of illegal purchase of VAT special invoices
Taking the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices as the keyword and the crime of jeopardizing tax collection and management as the condition, the author retrieved 12 open criminal cases from FY2021 to FY2022, of which 6 were from the coal industry, 3 from the renewable resources industry, and the remaining 3 were from the agricultural products industry, the trade industry, and the construction industry, respectively.
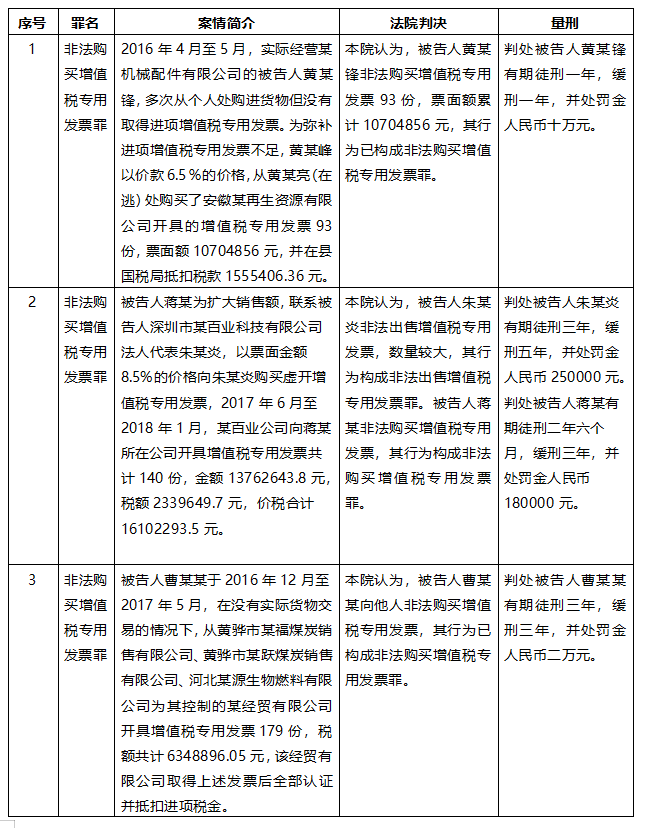
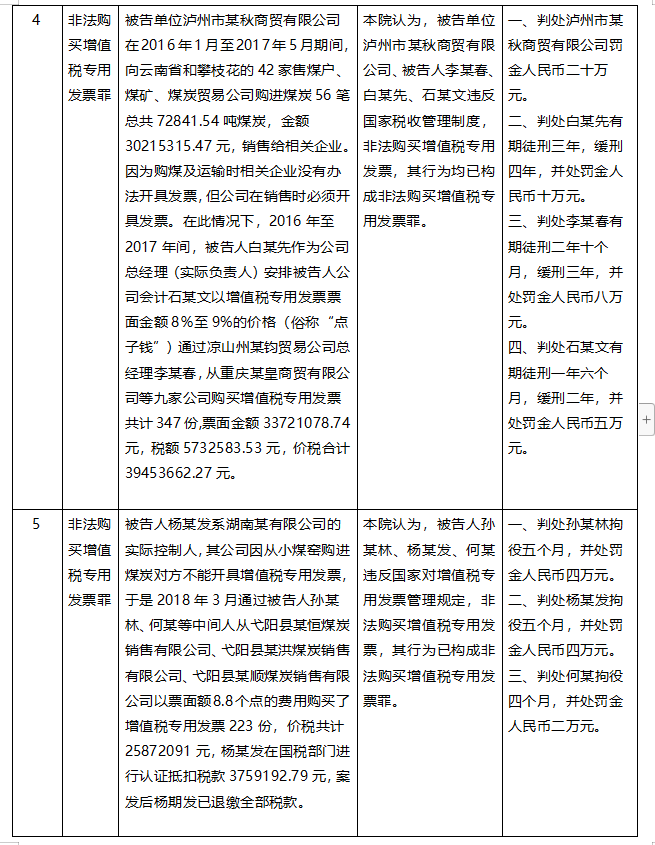
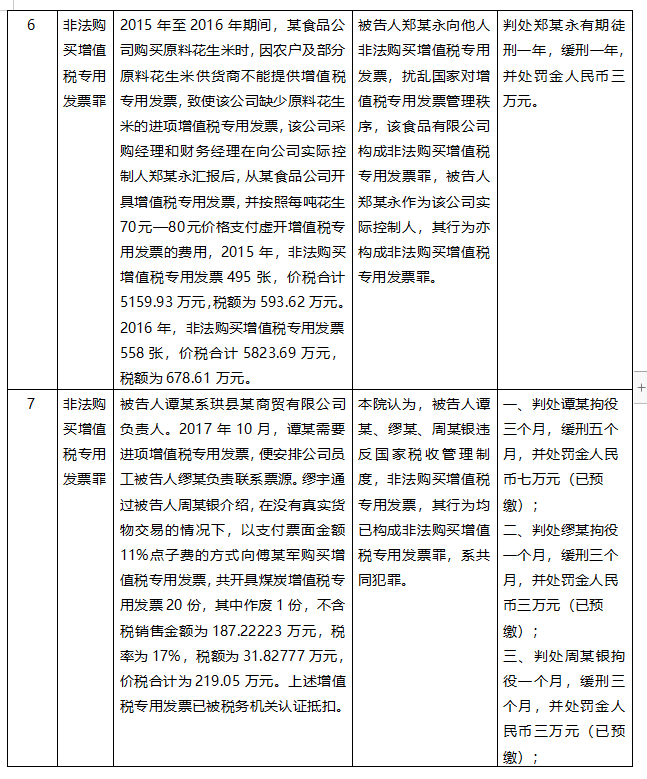
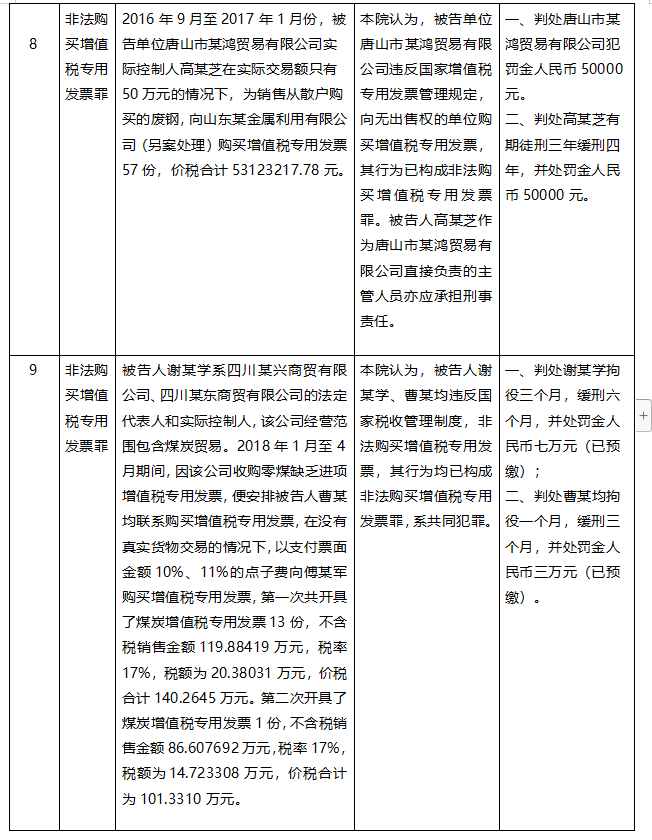
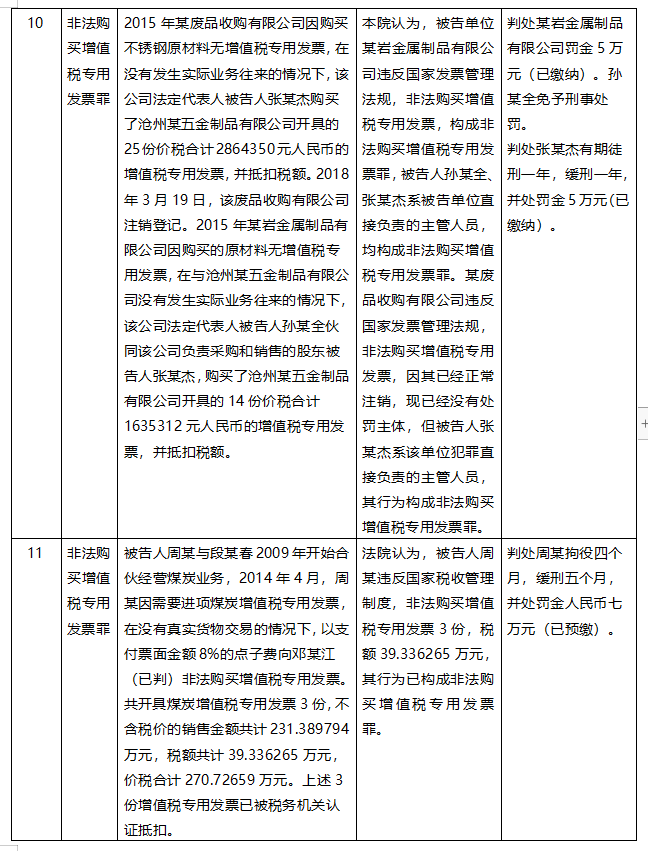

Through the introduction of the cases in the above cases, it can be found that this is similar to the practice of being judged as the crime of false VAT invoices in the business model, the behavior involved in the case, and many other aspects, so what is the basis of the court's final judgment for the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices?
II. the court ruled that the crime of illegally purchasing VAT invoices is based on the judgment point of view.
(I) There is a real transaction in the case
VAT is a kind of turnover tax which is levied on the basis of the value-added amount of commodities or taxable services in the process of turnover, and the collection of VAT should be based on the fact that there is an actual turnover of commodities or taxable services with value-added, and similarly, the issuance of VAT invoices should be based on the fact of the actual occurrence of the turnover of commodities or taxable services, and it is a kind of false invoicing behavior if VAT invoices are issued without a real trade. If the VAT invoices are issued without real trade, it is a kind of false issuance behavior, which is essentially a false issuance of VAT invoices. On the contrary, if the defendant's purchase of VAT invoices is based on real business and his subjectivity is not for the purpose of cheating state tax, it does not constitute the crime of false invoicing of VAT, and if it meets the constitutive elements of the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices, the defendant shall be convicted and sentenced for the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices.
(II) The defendants paid the tax in a timely manner, which objectively did not result in the loss of state tax.
Special VAT invoices can only be collected and purchased by general VAT taxpayers at designated tax authorities with corresponding vouchers, and no other units or individuals are allowed to commit the act of buying and selling special VAT invoices. Although according to the provisions of the Criminal Law, the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices infringes upon the strict system of purchasing VAT invoices in China, objectively requires that the perpetrator has committed the act of illegal purchase and sale, subjectively requires that the perpetrator has cognition of the act of illegal purchase, and whether or not the perpetrator has gained profit, for what purpose of the purchase and sale, and whether or not the loss of national tax has been caused is not a boundary between the crime and the non-crime of this crime. However, in judicial practice, whether or not to pay back taxes is usually considered by the court as a circumstance in sentencing. Taking the second previous case, the case of Jiang's illegal purchase of VAT invoices, as an example, the court ruled that: although the falsely issued VAT invoices involved in the case had all been certified for deduction, considering that Jiang purchased the VAT invoices in order to expand the company's performance, he had inflated the cost of the cell phones while increasing the sales price of the cell phones through the purchase of the VAT invoices. The available evidence could not exclude that the company acquired the fraudulent VAT special (input) invoices which were the VAT special (output) invoices that were offset against the company's increased sales price. Thus, on the ground that there was insufficient evidence for the company to certify the falsely issued VAT special (input) invoices for offsetting to determine that it caused the loss of state tax, the crime of falsely issuing VAT special invoices was not constituted, and the verdict was for the crime of illegally purchasing VAT special invoices.
(III) The defendant subjectively does not have the intention of tax fraud
The crime of false VAT invoice, as mentioned before, needs to cause the loss of national tax as the constitutive element, and in the crime of letting other people make false invoices for themselves, this tax loss mainly refers to the fact that the invoiced enterprise has deducted the input tax that should not be deducted. However, in the case of the type of false invoicing, the tax deducted by the enterprise purchasing the VAT input invoices is a transaction that actually occurred by itself, and thus objectively does not and cannot cause the loss of tax. Subjectively, the defendant is trying to offset the input tax of his own real business and does not aim at fraudulently offsetting the tax. Therefore, it cannot constitute the crime of false VAT invoicing. If the constituent elements of the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices are met, the defendant shall be convicted and sentenced for the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices. Article 208 of the Criminal Law does not make specific provisions on the elements of the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices. According to the Measures for the Administration of Invoices and the Provisions on the Use of VAT Special Purpose Invoices, VAT special purpose invoices can only be applied for by the tax authorities in accordance with the law, so it is feasible to incorporate this kind of "act of opening on behalf of the tax authorities" into the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices. Therefore, it is feasible to include this kind of "act of opening on behalf of others" in the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices. In judicial practice, there is no lack of cases in which illegal purchase of VAT invoices is defended as a misdemeanor.
However, it should be noted that when the author was combing through the above cases, he found that in the cases of illegal purchase of VAT invoices, there were cases of fund return, separation of invoices and goods, and payment of invoicing fee, which were similar to the cases of false opening of VAT invoices, and the reason why there was no judgment of false opening of VAT invoices, the court, in the judgment, mostly based on the fact that there were real transactions and the defendant's subjectivity. The court, in its judgment, mostly takes the existence of a real transaction, the subjective non-existence of the defendant's intention to cheat tax, the objective non-cause of the loss of national tax, and the timely payment of tax after the crime as the reason for the decision.
III. Insufficient input invoices in coal, renewable resources and agricultural products industry trigger tax-related risks
The actual tax burden of coal, renewable resources and other bulk trade industries is high, which is mainly caused by the characteristics of the industries. Coal mining industry and renewable resources recycling enterprises are located in the early stage of the whole industrial chain, with obvious characteristics of less VAT deductible inputs, thus stimulating the real demand for invoicing.
For coal enterprises, previously, because of the existence of quota system, coal enterprises can be able to purchase coal within the quota from regular large coal mines in the number of increasingly tense, so they have to purchase over-mining coal from small coal mines, and this mode of operation has led to a large number of small coal mines in excess of the quota of coal mining can not be sold in their own name and provide VAT invoices, which has resulted in the lack of deductible input of the industry of the coal enterprises. This has led to the industry problem of insufficient input deduction for coal enterprises. It is in order to realize the input deduction rights and interests that they have already obtained, some private coal enterprises have to remodel their business process, seek third-party cooperation and obtain VAT invoices to be used for cost deduction before enterprise income tax and VAT input deduction. It is this irregular business process that may lead to private enterprises being recognized by the judiciary as suspected of committing crimes.
The same is true for renewable resources recycling enterprises, as the waste materials operators are retailers or sellers (individuals who gather scattered household sources of goods), a considerable part of the retailers do not have the business license of individual industrial and commercial enterprises, and are unable to issue special VAT invoices. China had partially solved this problem by adopting a preferential policy for renewable resource enterprises, however, it was canceled around 2008 due to other shortcomings of the policy. Subsequently, preferential measures were also introduced in 2015, but the subsidies were moved back, and the policy of conditional instant VAT refund was only implemented for the renewable resources processing segment, and the policy of full levy for the renewable resources recycling segment has continued until today. As a result, the current recycling enterprises usually have difficulties in obtaining enough VAT input invoices for deduction, and the tax burden is too heavy. Statistics also show that the tax burden level of the waste and scrap industry is significantly higher than that of other industries.
For the agricultural products industry, the issuance of invoices for the acquisition of agricultural products is special. Some provinces stipulate that the invoices for the acquisition of agricultural products can only be used within the county (city or district), and those who acquire agricultural products across counties (cities or districts) can only ask for ordinary invoices from the sellers or apply for relevant certificates from the competent tax authorities, and then apply for acquisition invoices from the tax authorities of the place where the products are acquired. In order to circumvent the above invoicing restrictions, some cross-city and cross-provincial acquisition enterprises, after acquiring agricultural products from foreign provinces and cities, issue purchase invoices for agricultural products by utilizing the information of local natural persons engaged in agricultural production to meet the demand for deduction, which is prone to cause risks. In summary, under the special industry characteristics and current policy environment, coal, renewable resources and other industries have given rise to a large number of acts of issuing VAT invoices on behalf of others, which may constitute the crimes of "false opening of VAT invoices" and "illegal purchase of VAT invoices". ".
IV. The situation of tax collection and management is getting more and more severe, and enterprises should operate in a compliant manner in order to prevent legal risks.
(I) "Golden Tax IV" and Tax Big Data Strengthen Tax Governance
As the pilot of "all-electric invoice" continues to be rolled out and the development of "Golden Tax IV" is gradually completed, it will help realize the long-term mechanism of tax collection and administration with big data of "sharing, common construction and common governance". The construction of tax big data. The long-term behavior of enterprises can be summarized by big data to create a unique and personalized enterprise tax file, which can have a first-hand grasp of the enterprise's preferred scope of operation and geography, average profit margins, upstream and downstream enterprises, and other information. If an enterprise has special circumstances, such as too great a fluctuation in profits during the period, abnormalities in imports and sales, or one or more businesses "going in and out quickly," the early warning system may be triggered, which needs to be verified by the tax authorities. If an enterprise issues false invoices, the invoices from where they are issued, when they are certified, how they are circulated, and what goods are imported and exported respectively, all of them are retained in the "all-electric invoice" system, which can be cleaned up and investigated in time, so that the invoice information will be more transparent, and the traces of the circulation will be clearer, and the upstream and downstream full-chain tracing will be more easy. (ii) Enterprises should operate in a compliant manner.
(II) Enterprises should operate in compliance to prevent criminal risks
Enterprises should establish a perfect management system for VAT, EIT and small taxes as well as a voucher management system for VAT invoices and other vouchers based on business authenticity. Specifically, it includes: 1. Establishing an enterprise invoice management database for all tax types, entering all invoice information into the database through the upgrading of technology and equipment, and matching and verifying it with the enterprise's inventory, financial and other data, so as to provide comprehensive invoice information for the decision-making level of the enterprise as well as the personnel of the relevant positions; 2. Establishing a database of upstream and downstream enterprise's tax-related information, grasping the creditworthiness of upstream and downstream enterprises comprehensively, and actively Obtain the invoice data of the relevant enterprises to ensure that the transactions with the upstream and downstream are real and effective, and the invoice information is accurate; 3. Through technical means, the paper invoices and vouchers will be entered into the data system for preservation, and automatic archiving and verification will be realized, which is convenient for the financial department to access. In addition, enterprises should save relevant contracts, invoices, transportation documents, remittance slips and any other transaction-related information and evidence in their specific business, so as to achieve evidence retention.
(III) Enterprises should pay attention to tax audit and criminal investigation, and actively safeguard their legitimate rights and interests.
Looking at the criminal cases of false invoicing that have been decided, the court found that there are various cases constituting the crime of false invoicing of VAT, the crime of illegal purchase of VAT invoices and the crime of tax evasion. After in-depth study of the cases, it is found that the cases of the above different crimes have a lot of similarities in the business mode and behavior involved in the cases, and the problem of different judgments for the same case is also becoming more and more prominent in the field of tax-related crimes. In the author's opinion, for cases with real transaction basis, the situation that the perpetrator seeks a third party to issue VAT invoices should not constitute the crime of false VAT invoicing. This is because the perpetrators do not have the intention of cheating taxes, and most of them are only seeking to solve the problem of not being able to issue VAT invoices in the hope of gaining market competitiveness. Therefore, the judicial authorities should not only prudently grasp the purpose and result elements of the crime of illegally purchasing VAT invoices, but also consider the industry characteristics and business model of the bulk commodity trade, and prudently convict and sentence the offenders in accordance with the principle of modesty of the criminal law as well as the appropriateness of the crime and punishment, and for the practitioners of the industries of coal and renewable resources, they also need to practically understand the knowledge of the tax law, set up the awareness of risk prevention, and improve the level of lawfulness and compliance, as well as the current law. For practitioners in coal, renewable resources and other industries, they should also understand tax law, establish risk prevention awareness, improve legal compliance level, and have some basic understanding of the current legal practice to avoid falling into unnecessary criminal risks.





