Tax Lawyer Explained: New Implementing Rules of Invoice Management Measures Released, Five Major Revisions Worth Noting
On July 20, 2023, the State Council announced the newly revised Measures for the Administration of Invoices, and the Implementing Rules for the Measures for the Administration of Invoices, as a supporting regulation, was in urgent need of revision.On January 15, 2024, the State Administration of Taxation (SAT) announced the Decision on Revising the Implementing Rules for the Measures for the Administration of Invoices of the People's Republic of China (SAT Decree No. 56), which, in order to connect with the current laws and regulations In order to connect with the existing laws and regulations, it clarifies matters of concern to taxpayers, such as electronic invoice management, false invoicing, and the use of other vouchers in lieu of invoices. This article analyzes the provisions of the new Implementation Rules in order to clarify the rights and obligations of both parties, the invoicer and the third-party service organization, and better protect the legitimate rights and interests of taxpayers.
Change 1: Define the situation of "inconsistency with the actual operation of the business" to facilitate the definition of false invoicing behavior
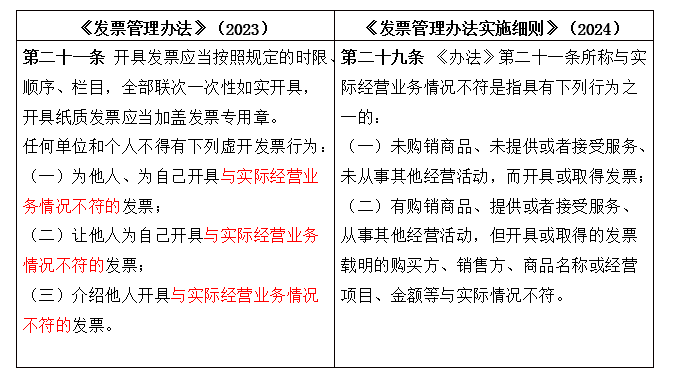
Measures Article 21 of the continuation of the previous definition of the scope of false invoicing behavior, the implementation of the rules supporting the amendments, Article 29 for the first time to clarify the "inconsistent with the actual business situation" of the specific meaning of both the purchase and sale of commodities, not to provide or accept services, not engaged in other business activities, while issuing or obtaining invoices, but also Including the purchase and sale of goods, provide or accept services, engaged in other business activities, but issued or obtained invoices contained in the buyer, seller, commodity name or business items, the amount of money and other cases inconsistent with the actual situation.
"No goods false invoicing" is inconsistent with the actual operation of the business situation needless to say. It is worth noting that "with goods on behalf of open" is also clearly defined as false opening behavior. In the field of renewable resources, coal, transportation and other areas, natural person retailers are common suppliers in the transaction chain, due to their tax awareness of the rule of law is not strong, the degree of tax compliance is generally not high, the purchasing side of the enterprise generally face the VAT input is not enough, can not get the pre-tax deduction of enterprise income tax vouchers of the trouble. Taking the renewable resources industry as an example, recycling enterprises are often unable to obtain invoices when purchasing waste materials from retailers, while downstream waste-using enterprises require recycling enterprises to issue invoices, and the tax cost of recycling enterprises has increased sharply in the case of broken VAT deduction chain. As a result, some recycling enterprises have begun to seek to issue special VAT invoices from third parties that are consistent with their procurement business. In the criminal field, it is usually argued that "truthful invoicing" is not false invoicing, so as to prevent the invoicing party and the invoiced party from pursuing the criminal liability for false invoicing. However, in the administrative field, with the implementation rules of the "and the actual operation of the business situation is not consistent with the" meaning of clear, "goods on behalf of the open" characterization of the fuzzy zone disappears, the existence of such behavior of taxpayers in the administrative risk of false invoicing is extremely difficult to avoid.
Change 2: Improvement of invoice violation penalty procedures, and the existing laws and regulations
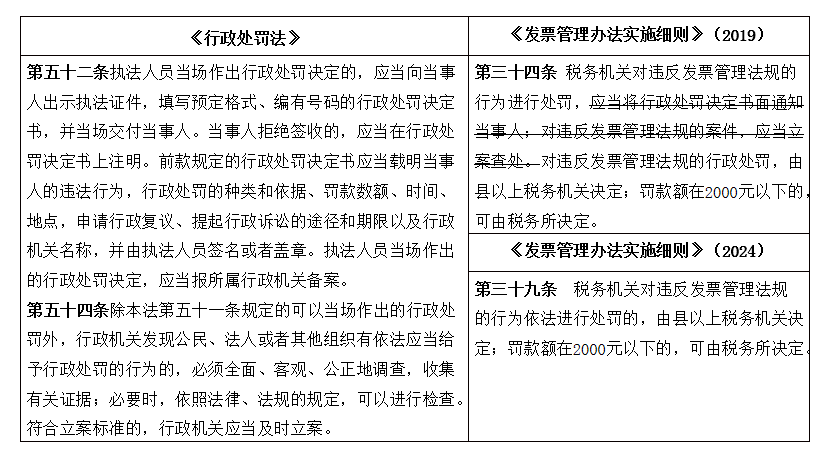
For one thing, article 52 of the Administrative Penalty Law clearly stipulates that the decision letter on administrative penalties to be made to the parties concerned shall contain the type and basis of administrative penalties, the amount of fines, the time and place, the means and time limit for applying for administrative reconsideration and instituting administrative litigation, as well as the name of the administrative organ, etc., and shall require that the decision letter be signed or stamped by the law enforcement officers. Therefore, the implementation rules have deleted the original "shall notify the party concerned in writing of the administrative penalty decision", and the tax authorities shall directly apply the provisions of the Administrative Penalty Law in making decisions on tax administrative penalties to taxpayers and so on.
Secondly, Article 54 of the Administrative Penalty Law stipulates the prerequisite of "meeting the criteria for filing a case" for administrative authorities to file a case to investigate and deal with a violation of the law, but the original implementation rules generally stipulate that "a case shall be filed and investigated for violation of the invoice management regulations", which ignores the fact that the case of violation of the invoice management regulations is not yet investigated and dealt with. However, the original Implementing Rules stipulated in general terms that "cases of violation of invoice management regulations shall be investigated and dealt with", ignoring the fact that some of the cases of violation of invoice management regulations did not meet the criteria for filing a case, and no case needed to be filed for application of summary penalties or the first violation of the law without penalties.
The newly amended implementing rules of Article 39 of the above deletion is conducive to the implementation of the rules and the provisions of the Administrative Penalty Law, improve the penalty procedures for invoice violations, and help to achieve the tax administrative penalties are not in vain and not indulgent.
Change 3: Refinement of the use of other vouchers in place of invoices, homemade vouchers in the accounts face penalties
According to Article 33(6) of the Measures, if other vouchers are used instead of invoices, the tax authorities have the right to order the perpetrator to make corrections, impose a fine of less than 10,000 yuan and confiscate the illegal income. Article 40 of the Implementing Rules has made detailed provisions on the behavior, specifying that if an invoice should be issued but not, or if other vouchers are used instead of invoices, or if other vouchers or homemade vouchers other than invoices are used for tax deduction, export tax rebate, pre-tax deductions and financial reimbursement, or if invoices that do not conform to the regulations are obtained and used for tax deduction, export tax rebate, pre-tax deductions and financial reimbursement, all of these belong to the behavior of using other vouchers in place of invoices. Instead of invoice use behavior.
Among them, the use of homemade vouchers instead of invoices is more common. For example, in the renewable resources industry, although the Announcement on Improving VAT Policies for Comprehensive Utilization of Resources (Announcement No. 40 of the Ministry of Finance and the State Administration of Taxation of 2021) has already given the recycling enterprises the qualification to choose the simplified tax method to calculate and pay the VAT according to the 3% levy rate, there are still some recycling enterprises that continue the original financial processing method, and carry out the pre-tax deduction by making the self-made acquisition vouchers and self-constructed acquisition ledgers. However, there are still some recycling enterprises continue the original financial treatment by making their own acquisition vouchers and building their own acquisition ledgers for pre-tax deduction.
According to Article 9 of the Announcement of the State Administration of Taxation on the Issuance of the Measures for the Administration of Pre-tax Deduction Vouchers for Enterprise Income Tax (Announcement No. 28 of 2018 of the State Administration of Taxation), if the expenditure items incurred by an enterprise within the territory belong to the value-added tax (VAT) taxable items, and if the other party is a VAT taxpayer that has applied for tax registration, the expenditure shall be made by means of invoices (including invoices issued by the tax authorities on behalf of the taxpayer in accordance with the provisions) as the pre-tax Deduction vouchers. The purchase of waste materials by renewable resources recycling enterprises belongs to VAT taxable items, and VAT invoices should be used as deduction vouchers. As a result, the tax authorities in some places no longer recognize the pre-tax deduction method that the recycling enterprises make their own purchase vouchers, or require the enterprises to provide the contracts, payment vouchers and other external vouchers corresponding to the purchasing business to support the authenticity of the transactions, or require them to reissue or replace the legal invoices, or even directly determine that the enterprises have not obtained the legal pre-tax vouchers, and are not allowed to carry out the pre-tax deduction, and then levy their enterprise Income tax and late payment charges. Therefore, the detailed provisions of Article 40 of the Implementing Rules may lead to the investigation and handling of various industries such as energy, renewable resources, agricultural products and other industries involving homemade vouchers instead of invoices, which will lead to huge administrative and criminal risks once it is verified that the enterprise constitutes tax evasion, tax cheating or false invoicing at the same time.
Change 4: The tax authorities have the right to adjust the type and amount of invoices used by taxpayers.
Article 18 of the Implementing Rules adds a new paragraph: "The tax authorities shall determine or adjust the types, quantities, amounts, and methods of invoices according to the tax risk level, tax credit level, and actual operation of the units and individuals," making it clear that the tax authorities can adjust the types and amounts of invoices used by taxpayers.
This provision is closely related to the current taxpayer classification management and tax credit rating system. According to Article 32 of the Measures for Tax Credit Management (for Trial Implementation) (Announcement No. 40 of 2014 of the State Administration of Taxation), "For taxpayers with a tax credit rating of D, the tax authorities shall take the following measures: (b) The collation of VAT special invoices shall be handled in accordance with the policy for general taxpayers during the counseling period, and the collation of ordinary invoices shall be carried out by handing over (checking) old invoices for supplying new ones, and in a strictly Limited supply". According to the "Policy for General Taxpayers in the Counseling Period", according to the "Measures for the Administration of the Counseling Period for General Taxpayers in Paying Value-added Tax" (Guoshuifa [2010] No. 40), the tax authorities shall strictly authorize the number of VAT special invoices for each time when the taxpayers apply for them.
In practice, taxpayers have been assessed as Class D due to their tax credit rating, which leads to strict restrictions on the number and amount of invoices issued, so that their normal business is seriously hindered. For example, a bulk commodity trading enterprise is suspected of the crime of false invoicing, and the tax authorities have restricted the invoices it can issue to a maximum of 100,000 yuan each, and there is a limit on the amount of special invoices it can issue each month. However, the enterprise usually sells huge amounts of goods and often needs to issue invoices of millions of dollars. As a result, the normal business of the enterprise cannot be carried out, which seriously affects its ability to carry out corporate compliance rectification.
Taxpayers should be reminded that the Announcement of the State Administration of Taxation on Matters Relating to Tax Credit Repair (SAT Announcement No. 37 of 2019) stipulates that if a taxpayer fails to pay or pays in full the taxes, late fees and fines in accordance with the conclusions of the tax authorities' processing, the tax credit level will be directly adjudicated as D. The tax credit level of the taxpayer will be determined as D. The tax credit level of the taxpayer will be determined as D. Among them, taxpayers who have not constituted a crime and are able to "pay the full amount or make up the payment within 60 days after the expiration of the time limit specified in the conclusion of the tax authority's handling" may apply for repairing the tax credit grade. Taxpayers should grasp the deadline to avoid being directly judged as Grade D due to tax arrears, which will affect the normal operation of enterprises.
Change 5: Complying with the reform of electronic invoicing and supporting the development of management system
On March 24, 2021, the Office of the Central People's Government and the State Council announced the Opinions on Further Deepening the Reform of Tax Collection and Administration, proposing "to take the reform of electronic invoicing as a breakthrough, to take tax big data as a driving force, to build an intelligent tax with high integrated functions, high security performance and high application effectiveness, and to comprehensively promote the digital upgrading of tax collection and administration and the transformation of intellectualization. "In December 2021, the pilot work of all-electronic invoicing began, and the national unified electronic invoice service platform was built. Since then, provinces and cities across the country have been carrying out pilot work on digital electric invoices and pilot work on all-store invoice acceptance. By November 29, 2023, the Tibet Autonomous Region Tax Bureau of the State Administration of Taxation issued the Announcement on the Pilot Work of Fully Digitized Electronic Invoices and its interpretation, determining that the pilot work of digital-electric invoicing would be officially launched on December 1, 2023, and the pilot work of digital-electric invoicing would be officially launched on December 1, 2023. As of this date, the pilot work on digital and electronic invoicing has completed the national provincial coverage.
On July 20, 2023, the newly amended Measures for the Administration of Invoices (the "Measures") started off by giving electronic invoices the same legal effect as paper invoices in the form of an administrative regulation and expressly authorizing the State Administration of Taxation to formulate implementation rules for the specific types of invoices, the number of invoices, their contents, coding rules, data standards, the scope of use, etc. The Measures were adopted by the State Administration of Taxation. The State Administration of Taxation is also expressly authorized to formulate implementation rules for the specific management methods of invoices, such as types of invoices, number of couples, contents, coding rules, data standards, scope of use, etc.
For one thing, the implementation rules clarify the basic management regulations of electronic invoices. On the basis of establishing the legal status of electronic invoice, Article 3 of the Implementing Rules further clarifies the definition of electronic invoice as "in the purchase and sale of commodities, provision or acceptance of services and other business activities, in accordance with the provisions of the invoice management of the tax authorities in the form of data messages issued and received vouchers for receipt and payment", and emphasizes that no unit or individual shall refuse to accept the electronic invoice. Individuals shall not refuse to accept electronic invoices. In terms of invoice management, Article 4 of the Implementing Rules specifies that the tax authorities have the responsibility to "build an electronic invoice service platform" and "provide services such as issuing, delivering and checking electronic invoices in digitized form".
At the National Tax Work Conference held on January 24-25, 2024, "steadily promoting the promotion and application of fully digitized electronic invoices and expanding the scope of the new nationwide unified e-tax bureau" remained the top priority of the national tax system in 2024 to promote modernized tax practices. As more and more enterprises start to use digital electronic invoices, traditional paper invoices will be replaced at an accelerated pace, which will not only significantly improve the efficiency of tax collection and management, but also enhance the supervisory effectiveness of invoice risks through the collection of tax-related information by tax authorities. The provisions of the implementation rules on the management of electronic invoices are precisely to maintain the above reform results and promote the "last kilometer" of the electronic invoice reform to go deeper and more practical, so that the results of the reform can really benefit all taxpayers.
Secondly, the Implementing Rules emphasize the provisions of sound invoice data security management. Article 5 of the Implementing Rules also adds provisions on invoice data security management, making it clear that tax authorities, units and individual taxpayers should safeguard the security of invoice data, in particular, taxpayers shall not violate the provisions of the use of invoice data, illegal sale or illegal provision of invoice data to others. In addition, Article 31 of the Implementing Rules also stipulates that third parties providing services such as invoice application and issuance shall also have the responsibility to "accept the supervision of the tax authorities".
With the implementation of digital invoices, the whole process and chain of invoices will be regulated. While taxpayers issue invoices and enter transaction information into the system, the review and processing of invoice data becomes the key support for the tax administration function of the tax authorities. On the one hand, through the information processing of individual invoice data, the tax department can collect taxes and fees on related transactions in accordance with the law. On the other hand, through the collection of various types of invoice information, and then the comprehensive integration, correlation and processing of invoice data and other tax-related data, it will become the tax big data support for tax departments around the world to realize accurate supervision. It is not difficult to find out from the information of cases notified by tax departments around the world that the precise analysis of clues by tax big data has become the main means to investigate and deal with tax-related crimes. In addition, as tax big data has the characteristics of covering the whole economic field, reflecting economic activities quickly, having high degree of data refinement and synthesis, and documenting economic activities accurately, these data are also valuable resources for macroeconomic decision-making. Therefore, the provisions of the implementing rules on sound invoice data security management are not only conducive to tax collection and management and the optimization of tax and fee services, but are also the basis for macroeconomic decision-making.
Currently, the use of digital and electronic invoices for false invoicing has bubbled up, and in June and August 2023, the Shenzhen tax department and the Jilin provincial tax department announced a case of false invoicing of fully digitized electronic invoices, respectively. As digital and electronic invoices flow automatically in the system, the invoice data is associated with upstream and downstream enterprises, and an enterprise suspected of false invoicing, the whole chain can hardly be left alone.





